
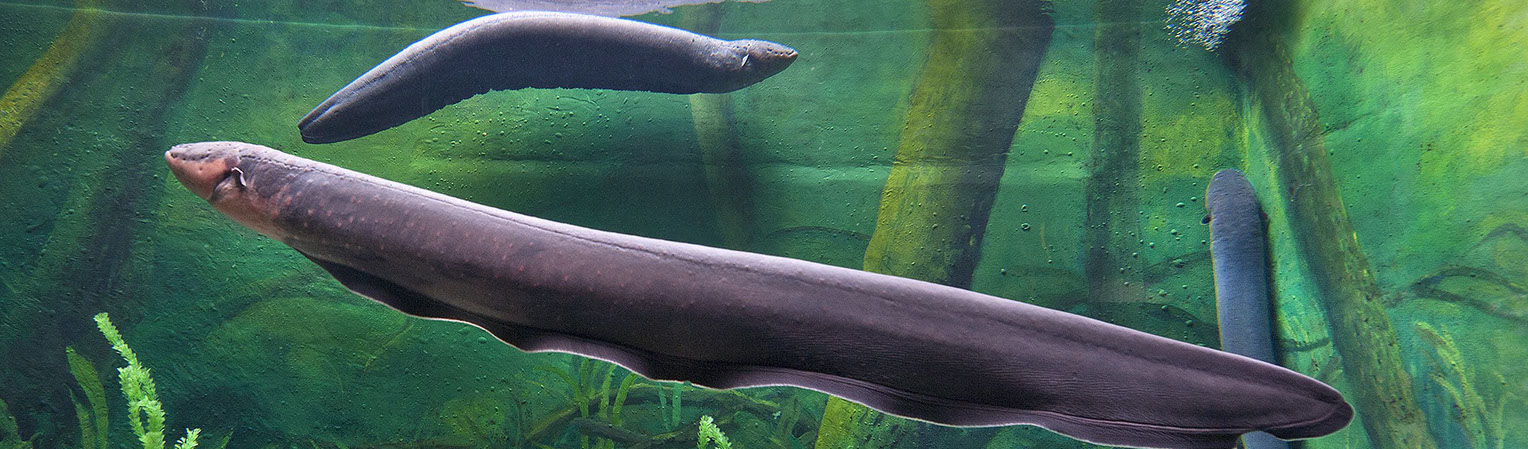

Gene 686 (2019) 164-170
Mitogenomics of Central American weakly-electric fishes
Celestino Aguilara, Matthew J. Miller, Jose R. Loaiza, Rüdiger Krahe, Luis F. De León.
Abstract:
Electric fishes are a diverse group of freshwater organisms with the ability to generate electric organ discharges (EODs) that are used for communication and electrolocation. This group (ca. 200 species) has originated in South America, and six species colonized the Central American Isthmus. Here, we assembled the complete mitochondrial genomes (mitogenomes) for three Central American electric fishes (i.e. Sternopygus dariensis, Brachyhypopomus occidentalis, and Apteronotus rostratus), and, based on these data, explored their phylogenetic position among Gymnotiformes. The three mitogenomes show the same gene order, as reported for other fishes, with a size ranging from 16,631 to 17,093 bp. We uncovered a novel 60 bp intergenic spacer (IGS) located between the COII and tRNALys genes, which appears to be unique to the Apteronotidae. Furthermore, phylogenetic relationships supported the traditional monophyly of Gymnotiformes, with the three species positioned within their respective family. In addition, the genus Apteronotus belongs to the early diverging lineage of the order. Finally, we found high sequence divergence (13%) between our B. occidentalis specimen and a sequence previously reported in GenBank, suggesting that the prior mitogenome of B. occidentalis represents a different South American species. Indeed, phylogenetic analyses using Cytochrome b gene across the genus placed the previously reported individual within B. bennetti. Our study provides novel mitogenome resources that will advance our understanding of the diversity and phylogenetic history of Neotropical fishes.
Scientific Reports (2019) 9:18828
Tempo and mode of allopatric divergence in the weakly electric
fish Sternopygus dariensis in the Isthmus of Panama
Celestino Aguilar, Matthew J. Miller, Jose R. Loaiza, Rigoberto González, Rüdiger Krahe, Luis F. De León.
Abstract:
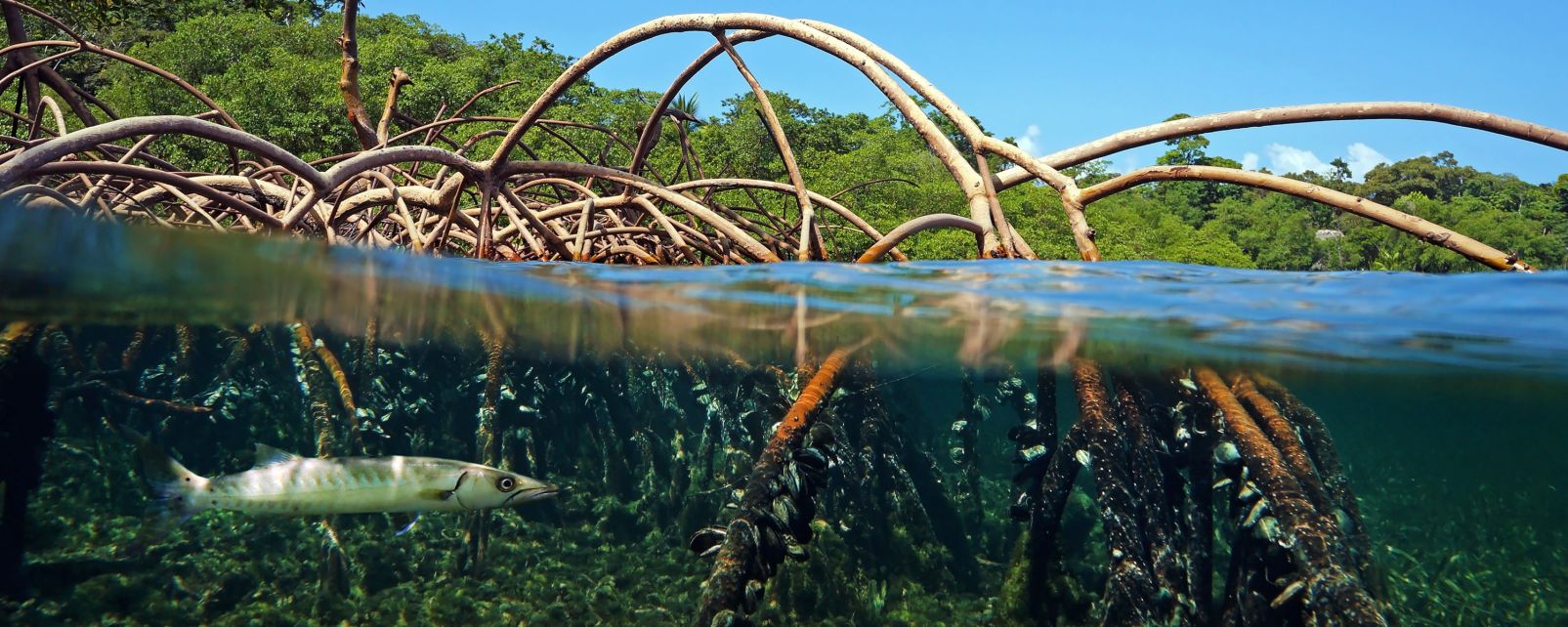
Spatial isolation is one of the main drivers of allopatric speciation, but the extent to which spatiallysegregated populations accumulate genetic differences relevant to speciation is not always clear. We used data from ultraconserved elements (UCEs) and whole mitochondrial genomes (i.e., mitogenomes) to explore genetic variation among allopatric populations of the weakly electric fish Sternopygus dariensis across the Isthmus of Panama. We found strong genetic divergence between eastern and western populations of S. dariensis. Over 77% of the UCE loci examined were differentially fixed between populations, and these loci appear to be distributed across the species’ genome. Population divergence occurred within the last 1.1 million years, perhaps due to global glaciation oscillations during the Pleistocene. Our results are consistent with a pattern of genetic differentiation under strict geographic isolation, and suggest the presence of incipient allopatric species within S. dariensis. Genetic divergence in S. dariensis likely occurred in situ, long after the closure of the Isthmus of Panama. Our study highlights the contribution of spatial isolation and vicariance to promoting rapid diversification in Neotropical freshwater fishes. The study of spatially-segregated populations within the Isthmus of Panama could reveal how genetic differences accumulate as allopatric speciation proceeds.

Tel: (507) 5170700 - Fax: (507) 5070020 - EFax: (507) 5170701 | INDICASAT - AIP | Edificio 219, Ciudad del Saber | Clayton, Apartado 0843-01103 | Panamá 5 Panamá, Rep. de Panamá.
© Copyright 2014. INDICASAT AIP. Todos los derechos reservados.
INDICASAT.org.pa

Quienes somos
Síguenos